|
Biodiversity Information Science and Standards : Conference Abstract
|
|
Corresponding author: Wolf-Henning Kusber (w.h.kusber@bgbm.org)
Received: 13 Jun 2019 | Published: 21 Jun 2019
© 2019 Wolf-Henning Kusber, Andreas Kohlbecker, Heba Mohamad, Anton Güntsch, Walter G. Berendsohn, Regine Jahn
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Citation: Kusber W, Kohlbecker A, Mohamad H, Güntsch A, Berendsohn W, Jahn R (2019) Registration of Algal Novelties in Phycobank: Serving the scientific community and filling gaps in the global names backbone. Biodiversity Information Science and Standards 3: e37285. https://doi.org/10.3897/biss.3.37285
|
|
Abstract
The International Code of Nomenclature (ICN) for algae, fungi, and plants provides for nomenclatural indexing through nomenclatural repositories (
Thus, PhycoBank has been advocated by different players such as the International Society for Diatom Research (ISDR), the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF), and the Special Committee on Registration of Algal and Plant Names (including fossils). Aided by a grant from the German Research Foundation (DFG, JA 874/8-1), PhycoBank has been established at the BGBM Berlin as the repository for nomenclatural acts of algae. As added value, PhycoBank deals with orthographical variants in linking the published spelling of a name to the corrected one with reference to the respective article of the ICN (
Almost all nomenclatural acts are the result of taxonomic issues but also have implications for the taxonomic work of specialists worldwide. The challenge for implementing a registration system like PhycoBank is to inform individual scientists as well as to feed data into data networks, to strengthen their underlying names backbone linking scientific names to occurrences.
Since June 2018, PhycoBank staff are operating the registration system using a user-friendly data entry web application. This interface for data entry by volunteers has been available since March 2019. All data entered into the system undergoes a curatorial process to assure a high level of data quality.
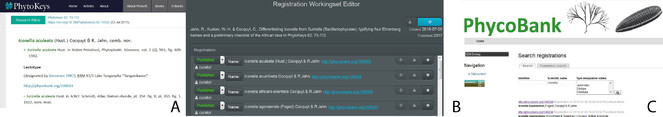
The data entry web application is complemented by a public data access portal which is available under https://www.phycobank.org (Fig.
PhycoBank workflow. A. Publication including a PhycoBank identifier, B. Registration User Interface, C. PhycoBank Portal. A and B link to C, C links back to A.
PhycoBank assigns resolvable and globally unique HTTP-based identifiers for nomenclatural acts, e.g. for the genus Iconella, https://phycobank.org/100040. Via these PhycoBank identifiers, the corresponding data and metadata can be retrieved in human- and machine-readable formats.
More than ten journals have published PhycoBank identifiers so far, allowing cross-linking between their PDF and the PhycoBank system. The Pensoft journals are pioneering an automatic registration workflow modeled and specified by the PhycoBank team.
Classifications are frequently subject to changes. Currently, the algal classification is under discussion because of results from phylogenetic research. PhycoBank aims to be neutral with respect to higher classification, but tracks classification information of each name that is registered into a directed graph of available higher rank names to record fragments of higher classification information and to facilitate search functionalities.
All scientists, editors, and publishers involved in the publication of nomenclatural novelties are invited to contact PhycoBank (curation@phycobank.org) to influence the prototypical registration process and to improve PhycoBank’s functionality.
Keywords
nomenclature, registration, names backbone
Presenting author
Wolf-Henning Kusber
Presented at
Biodiversity_Next 2019
References
-
International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (Shenzhen Code) adopted by the Nineteenth International Botanical Congress Shenzhen, China, July 2017.Koeltz Botanical Books,Glashütten. https://doi.org/10.12705/code.2018