|
Biodiversity Information Science and Standards : Conference Abstract
|
|
Corresponding author: Anniina Kuusijärvi (anniina.kuusijarvi@helsinki.fi)
Received: 03 Jun 2019 | Published: 13 Jun 2019
© 2019 Anniina Kuusijärvi, Ville-Matti Riihikoski, Samuli Lehtonen, Gunilla Ståhls, Marko Hyvärinen, Mikko Heikkinen, Leif Schulman
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Citation: Kuusijärvi A, Riihikoski V, Lehtonen S, Ståhls G, Hyvärinen M, Heikkinen M, Schulman L (2019) Database Tools to Meet the Nagoya Protocol Requirements in a Collection Management System. Biodiversity Information Science and Standards 3: e36734. https://doi.org/10.3897/biss.3.36734
|
|
Abstract
The Nagoya Protocol (NP) of the Convention on Biological Diversity requires that genetic resource holders and users obtain, preserve and keep relevant documentation. Users and third parties need to be informed on terms of access, which utilisation is allowed, and which benefits need to be shared when respective genetic resources or associated traditional knowledge is utilised in the meaning of the NP. Following the recommendations in the Code of Conduct & Best Practices of the Consortium of European Taxonomic Facilities (CETAF)
The Kotka CMS is used for storing and managing specimen data and for handling material transactions (loans, exchanges, donations and consumptive loans). Users can enter and store all necessary documentation for both incoming and outgoing material as material transactions, which hold information on e.g., the transaction type, description of the material, important dates, correspondent organization and contact person. Specimens are linked to transactions by their unique identifiers and each transaction also has a unique stable identifier. The first version of the tools for meeting the requirements of the Nagoya protocol on both in situ and ex situ accession of genetic resources have been integrated into the transaction section of the system.
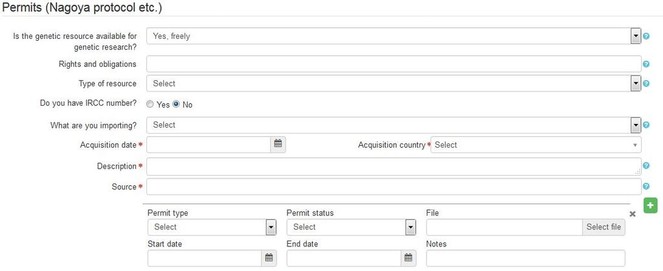
For genetic resource users to be able to enter, save and provide all the required information about an incoming genetic resource, we have implemented a set of fields to be completed in the transactions in Kotka CMS (Fig.
All the documentation and conditions regulating the utilisation of each specimen and derived samples must follow with the specimen data at all times. To accomplish this all the necessary information and documents are linked from the material transactions to the relevant specimens by unique specimen or sample identifiers. In the specimen view page, links to the full transaction details and history are given, as a single specimen or a derived sample can be part of several different types of transactions. Users also see a summary of the transaction information directly in the specimen view, most importantly whether the specimen is available for genetic research or has any restrictions for use.
The Kotka CMS transaction section makes use of the Application Programming Interface (API) provided by the Access and Benefit Sharing Clearing House (ABS-CH). Using the API, Kotka CMS validates the IRCC number if given and provides links to the ABS-CH, for example to the relevant country profile page, the contact details of the CNA, and specific requirements for access to genetic resources when applicable. This way, we provide Kotka CMS users up-to-date information from the original source to support their genetic resource management.
We will further improve and develop the tools during the years 2019-2020. Now that the first version is in use, we will make adjustments according to user feedback. We also have a few changes planned, for example, the tools for transferring the necessary information on permits and other details with outgoing specimens to a user in another institution abroad will be updated. All users in Finnish natural history institutions have access to all the information directly in Kotka CMS, as it is a national system. Additionally, both specimen and transaction information searchability will be refined.
Keywords
access and benefit sharing, collection management system, Nagoya Protocol
Presenting author
Anniina Kuusijärvi
Presented at
Biodiversity_Next 2019
References
-
Natural Science Collections and Access and Benefit Sharing. https://www.cetaf.org/services/natural-science-collections-and-access-and-benefit-sharing